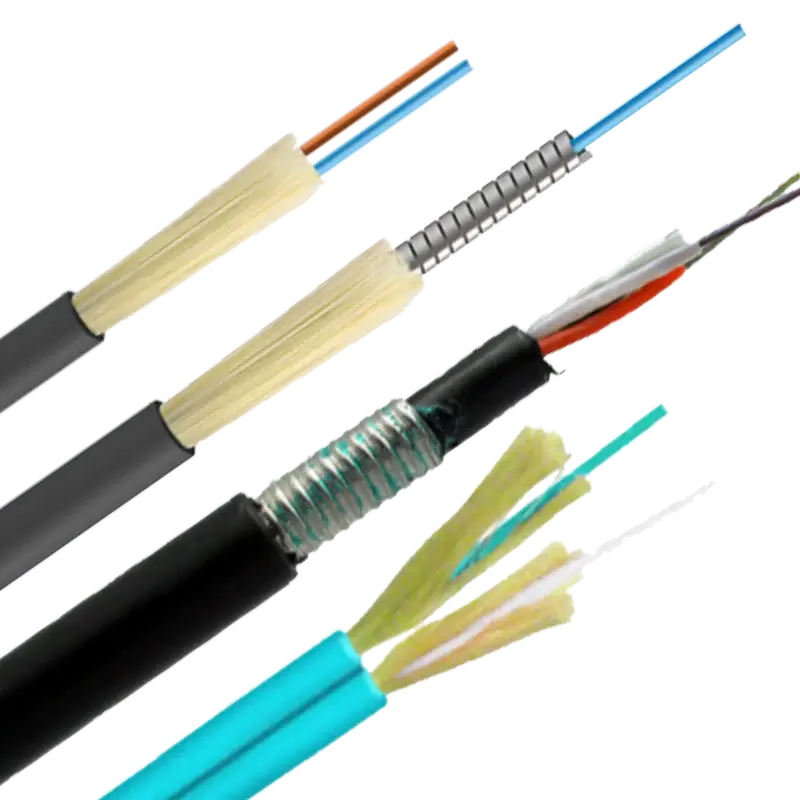
Fibre optic cables have revolutionized the way we transmit data, transforming everything from internet connections to telecommunications, healthcare, and even entertainment. But what exactly are fibre optic cables? How did they come about, and how are they shaping the world today? Let's explore the history, types, uses, and the growing market for fibre optics.
The History of Fibre Optic Cable
The concept of using light to transmit information dates back to the 19th century when Alexander Graham Bell invented the "Photophone" in 1880. This device was an early attempt to send sound via light waves. However, it wasn’t until the 1960s that the development of glass fibers and laser technology enabled practical use of fibre optics.
In 1970, researchers at Corning Incorporated developed the first practical fibre optic cable, capable of carrying signals over long distances. By the 1980s, fibre optic cables began to replace traditional copper wires in telecommunications, offering unprecedented bandwidth and speed. The continued improvement of materials, such as using pure silica glass, led to the modern fibre optic cables we know today.
Question to ponder: How has fibre optic technology impacted the evolution of communication over the last 50 years?
Types of Fibre Optic Cable
There are two primary types of fibre optic cables, each suited for specific applications:
1. Single-Mode Fibre (SMF):
Definition: Single-mode fibre has a small core (around 8-10 microns) and transmits data via a single light wave.
Best for: Long-distance communication. Single-mode fibre can carry signals over hundreds of kilometers without losing strength.
Example applications: Long-distance telecommunications, submarine cable systems, and internet backbone connections.
2. Multi-Mode Fibre (MMF):
Definition: Multi-mode fibre has a larger core (50-62.5 microns) and transmits data using multiple light waves.
Best for: Short-distance communication. Multi-mode fibre is commonly used in local area networks (LANs) and data centers.
Example applications: Office networks, campus data centers, and internal building wiring.
Question to consider: Could the distinction between single-mode and multi-mode fibres be a key factor in developing the next generation of high-speed internet?
Uses of Fibre Optic Cables
Fibre optic cables have a wide array of applications across different industries. Here are a few of the most significant uses:
1. Telecommunications:
Fibre optics are the backbone of global telecommunications. High-speed internet, VoIP, and mobile data are all dependent on the vast fibre optic networks connecting cities and countries.
2. Medical Technology:
Fibre optics are crucial in medical imaging and diagnostics, particularly in endoscopy. They allow doctors to see inside the human body without invasive surgery.
3. Military and Aerospace:
Fibre optic cables are used in secure communication systems for the military. They are resistant to interference and provide higher security for sensitive data transmissions.
4. Entertainment and Broadcasting:
From cable TV to streaming services, fibre optics are critical for delivering high-quality video content at lightning speeds. They enable the smooth transmission of HD, 4K, and even 8K video formats.
Open thought: How would daily life be different without the widespread implementation of fibre optic technology in the media and telecommunications industries?
Fibre Optic Markets
The demand for fibre optic cables continues to grow across various markets. Here are some of the key industries utilizing this technology:
1. Telecommunications:
This is the largest market for fibre optic cables, driven by the global need for faster, more reliable internet and mobile data services.
2. Data Centers:
As cloud computing and big data expand, data centers rely on fibre optics for high-speed data transfer and storage.
3. Healthcare:
Fibre optics enable advanced medical imaging techniques, improving the precision of diagnoses and surgeries. The healthcare industry is increasingly adopting these technologies for real-time, high-resolution imaging.
4. Industrial Automation:
Factories and production facilities use fibre optics to manage data-heavy automation systems. Fibre optics are ideal in harsh environments because they are resistant to electromagnetic interference.
5. Smart Cities:
As cities worldwide adopt smart technologies, fibre optics support the real-time data transmission needed for traffic management, public safety, and energy efficiency systems.
Question to explore: With the rise of 5G and smart cities, how will the future demand for fibre optic infrastructure evolve?
Final Thoughts
Fibre optic technology has transformed communication, healthcare, and entertainment in unimaginable ways. As we move further into an era driven by connectivity, fibre optics will continue to play a key role in shaping the future.
But the conversation doesn't stop here! How do you think fibre optics will impact emerging technologies like virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and quantum computing? Could they become the foundation for the next major tech revolution?